
|
|
|
Gediz University, Computer Engineering
Department
Fall
Semester 2013
Lecture:
Tuesday:
14:00 - 16:45,
A-Z11, Lab:
Wednesday:
09:00 - 10:45,
E-NETWRLAB
|
| |
|
|
Instructor: Halûk
Gümüşkaya |
Teaching Assistant:
Arzum Karataş |
|
Office:
D107 |
Office: |
|
Office Hours: |
Office Hours: |
|
Phone:
0232-355 0000 - 2305 |
Phone:
|
|
e-mail: haluk.gumuskaya@gediz.edu.tr |
e-mail: arzum.karatas@gediz.edu.tr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Course Description
An overview of software
engineering, software life cycle, and methodologies. Modeling with UML
and design patterns, project management and software development, team
organization, requirements elicitation and analysis, system design,
object design, software testing. Software engineering concepts are
realized on a nontrivial team design project in which a group of
students implements a system from its specification and design using a
UML modeling and implementation tool.
Course Objectives
This course is an introduction to software engineering
using a large team project.
You will briefly learn
classical approaches in software development:
 |
The phases
of software development (the software "lifecycle")
|
 |
Software
requirements elicitation, analysis and specification |
 |
Design
concepts and techniques, including Unified Modeling Language (UML) and
Design Patterns |
 |
Implementation practices such as using a modeling tool with design
patterns and frameworks |
 |
Testing,
verification, and quality assurance (QA) techniques |
 |
Software
tools for software engineering and rapid development |
 |
Team and
management skills for completing a project in a large team
|
You will mainly learn and apply much modern agile
approaches and techniques in software development:
 |
Software Engineering
Principles by understanding new challenges, opportunities, and open
problems of SaaS (Software as a Service)
|
 |
Develop a SaaS
project from conception to public deployment using an
Agile Approach
Solve non-technical customer problems
Server side: Ruby on Rails
*
Client side: HTML, CSS, AJAX, JavaScript
Deploy using Cloud
Computing
*
Wikipedia: "In 2011, Gartner Research noted that despite criticisms and
comparisons to Java, many high-profile consumer web firms are using Ruby
on Rails to build agile, scalable web applications. Some of the largest
sites running Ruby on Rails include Github, Yammer, Scribd, Groupon,
Shopify, and Basecamp. As of March 2013, it is
estimated that about 211,295 web sites are running Ruby on Rails."
|
 |
Important Note:
|
I gave my
first Software Engieering (SENG) course about 10 years ago at Fatih
University. There were
54 students in my first SENG course. Some (5 as far as I know in
2013) of them obtained Ph.D. degrees and became academicians, and some
others became engineers and other professionals. There were
11 project teams following agile (like XP) or heavy (like RUP)
software development approaches in that course project. They put their
projects' work products to their project web sites.
One of the best project web sites
still lives today. This web site
has their work products;
by looking at these products we can learn their products and software
development process.
My course web pages, the
communication between me and students,
this student project web site and
their work products
give a quite good idea about typical development techniques (like Java,
graphical notation UML, Design Patterns, ..), processes and work
products advised for a good process-based software project development
in last 10 years. I finally followed this approach in the last year:
Look at the
syllabus, overview and
introduction lecture
slides of COM 401 Software Engineering course at Gediz University.
We have seen many new developments in the
last 10 years:
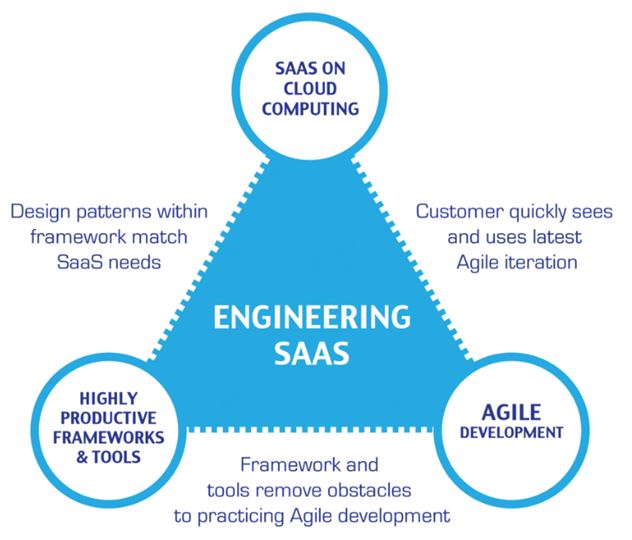
Developing Software as a Service (SaaS)
Enabling technologies:
- more web
centric software development and new web technologies (Ruby, …)
- service
oriented architecture and web services
- cloud
computing
-
hardware/software virtualization, multi-core computing, …
Agile Software Development as a
first class citizen
Enabling technologies:
-
highly productive frameworks and tools remove obstacles to practicing
Agile development
-
software development based on open source projects and legacy projects
Now, it is time for a
quite big deviation from my 10-year classical teaching approach
in software engineering courses that I have been giving since 2003...
Prerequisites
None
(officially, but it requires knowledge and practical experience gained
in COM 303 Advanced Programming)
Lecture Schedule
(tentative)
 |
This is the tentative lecture schedule.
Please check this page at least once a week during the semester. |
Textbooks
Required
Recommended
 |
Object-Oriented Software Engineering:
Conquering Complex and Changing Systems, Using UML, Patterns, and Java,
3rd Edition,
B. Brügge,
A. H. Dutoit, Prentice-Hall, 2010. (My classical textbook that I
used since 2003) |
 |
Practical Software Engineering:
A Case Study Approach,
L. Maciaszek, B. L. Liong, Addison Wesley, 864 pages, 2004. (This was my
second classical textbook). |
 |
Requirements Analysis and Systems
Design, 3rd Edition, L. Maciaszek, Addison-Wesley, 656 pages, 2007. |
 |
Object-Oriented Software Engineering: Practical Software Development
Using UML And Java, Timothy C. Lethbridge,
Robert Laganiere,
2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2004.
resources
|
 |
Applying
UML and Patterns: An Introduction to Object-Oriented Analysis and Design
and Iterative Development, Craig Larman, Prentice Hall, 2004. |
 |
Software
Engineering: An Object-Oriented Perspective, Braude, Ertic J.,
John Wiley, 2002.
resources |
 |
... |
Tools and Development Environments
Ruby on Rails Tools
 |
Aptana Studio
3 - web application IDE, harnesses the flexibility of Eclipse and
supports the latest browser technology specs such as HTML5, CSS3,
JavaScript, Ruby, Rails, PHP and Python. |
 |
RubyInstaller for Windows - includes the Ruby language, an execution
environment, important documentation. |
 |
Ruby
Miner - Intelligent Ruby and Rails IDE.
|
Project Management,
Analysis, Design, Coding and Testing Tools
Several
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) and
Test-Driven Development (TDD)
tools will be used:
Tools Used:
 |
Cucumber -
testing tool for running automated acceptance tests |
 |
RSpec - testing tool for writing unit tests
|
 |
Git - Version
control system |
 |
GitHub and
ProjectLocker -
Subversion Hosting, Git Hosting and project management - Cloud Development
Made Easy |
Other Possible Tools:
 |
Velocity - capacity planning tool used in agile software development
|
 |
Autotest - test automation tool
|
 |
SimpleCov - test coverage measurement tool
|
Some of the typical classical tools used
in the past:
Grading
15
% : Homework Assignments
20 % : Midterm
35
% : Project
30
% : Final Exam (a
comprehensive exam at the end of the course)
Project
See the lecture
schedule for the specific due dates of each
milestone.
The project milestones are
described below:
 | Iteration 0: initial customer meetings
1. Organize your team using Scrum
2. Meet with customer to discuss app
3. Summarize meeting and create
initial
User Stories on 3x5 cards
4. Create public Pivotal Tracker project and enter initial
User Stories
5. Optional for bonus credit: Produce 2-minute video interview
where customer describes problem your app will solve
6. Create lo-fi
UI Mockups and Storyboards for User Stories
7. Populate initial public GitHub repo for your project
|
 | Iterations 1-3: Team evaluation
points:
1. Project Management using Scrum
2. Using Pivotal Tracker identifying subset of User
Stories and completing them on this iteration and who owns each
3. UI Mockups and
Storyboards for User Stories
4. Use of BDD+TDD to develop these stories
4.1. BDD: Cucumber/Capybara/Mechanize -
Acceptance and Integration Tests
4.2. TDD:
RSpec (Unit Tests)
4.3.
Coding: Software Quality (Code Smells, SOFA, Metrics):
-
Following Ruby coding style
-
Code Documentation using RDoc
-
Qualitative Code Evaluation: SOFA: Use reek to find code smells
and refactor your code if necessary
-
Quantitative Code Evaluation:
- Calculate ABC Complexity using floog and refactor your
code if necessary
- Calculate Cyclomatic Complexity using saikuro and
refactor your code if necessary
- Use other quantitative metrics to improve your code quality
5. Upload project work products to public GitHub repository
6. Deploy working project prototype to Heroku cloud
platform
7. Get feedback from customer and indicate how this will affect
next iteration
8. Team self-evaluation
|
|
