|
|
|
BİLM 362 Bilgisayar Ağları
Fatih University, Computer Engineering
Department
Spring Semester
2008
CENG 362:
Tuesday
12:00 - 13:00 E -210,
Wednesday 08:00 - 10:00 E-210
BİLM 362:
Tuesday
08:00 - 10:00 E-217,
Wednesday 10:00 - 11:00 E-217 |
|
Instructor: Halûk
Gümüşkaya
|
Teaching and Lab Assistants:
CENG 362:
BILM 362: |
|
|
|
Mostly
Static Information: |
Mostly
Dynamic Information: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Grades-CENG362
Notlar-BILM362 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Course Description
Catalog Description:
OSI reference model, Internet and TCP/IP.
Application layer protocols: HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and DNS. Socket
programming, transport layer services, flow and congestion control, network
layer and IP protocol, addressing, routing, data link layer protocols, local
area networks.
Details
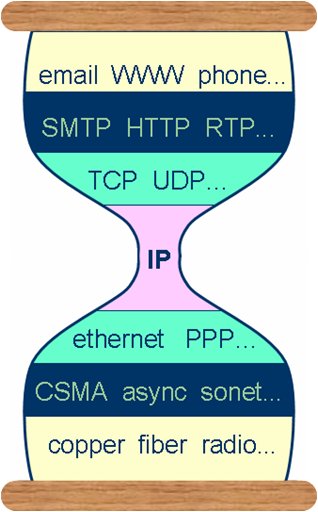
The Internet (TCP/IP)
Protocol Hourglass
This course provides an introduction to fundamental concepts in the design
and implementation of computer communication networks, their protocols, and
applications. Topics to be covered include: Introduction to computer
networks and the Internet, principles of application layer protocols,
TCP/UDP socket programming, DNS, HTTP, FTP, SMTP/POP3, transport layer services,
congestion control, network layer and IP protocol, addressing,
routing, data link layer protocols, local area networks. Examples will be drawn primarily from the Internet
protocol suite (e.g. HTTP, SMTP, TCP, UDP, IP) using
Wireshark,
a network
protocol
analyzer program and the Java
programming language.
The following lab experiments will be conducted
in our Computer Networks Lab:
Single Segment IP Networks, Static Routing, Dynamic Routing Protocols (RIP,
OSPF and BGP), LAN Switching, Transport Protocols (UDP and TCP), NAT and
DHCP, The Domain Name System.
CENG/BİLM 362 is a one-semester introduction to
computer networking theory, applications, and programming with a focus on
the Internet and its applications. It covers networking topics beginning from the
application-layer then going down the protocol stack (a top-down approach), allowing computer
engineering students to
quickly write networking applications while learning the theory and practice
of computer networking. Programming in Java is an important component
of the course. Some educational multimedia materials, network programs and
simulators will be also used to teach the networking fundamentals.
This is an advanced undergraduate course for
mainly computer engineering students. It is an introductory computer
networks course and serves as a pre-requisite for more advanced computer
networking topics. It may also be taken by interested non-CENG students who
have taken the pre-requisite courses (and its pre-requisites).
Prerequisites
 |
A basic understanding of
algorithms (CENG 201/202 Data Structures and Algorithms) and operating
systems (CENG 341 Operating Systems) is required. |
 |
A previous course in
computer organization (e.g. CENG 252) is required. |
 |
You must be able to program
in a structured high-level programming language, especially Java.
|
Lecture Schedule
This is the
tentative schedule. Please
check it once before the lecture
Textbooks
Main Textbooks
 |
Computer Networking: A
Top-Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 4th Edition (new
edition),
J. F. Kurose,
K. W.
Ross, Addison Wesley, 2007. |
 |
Bilgisayar
Ağları, Birinci Baskı,
J. F. Kurose,
K. W.
Ross, ALFA, 2007. (The main textbook's Turkish translation for BİLM 362 students, but they can
also use the
original book, it is much better to read the original book.) |
 |
Mastering Networks: An Internet Lab Manual,
J. Liebeherr,
M. E. Zarki,
Addison-Wesley, 2004, ISBN: 0-201-78134-4. (Lab book) |
 |
Java Ağ Programcılığı,
Haluk Gümüşkaya, Ömer Boyacı, 720 sayfa, 1. Baskı: Haziran 2003, ALFA.
(TCP/UDP Socket programming examples, and other chapters on Java I/O
Streams and Mutithreading from this book are very useful to understand
network programming concepts in Java.)
|
Recommended
 |
Computer Networks: A Systems Approach (4th Edition),
L. Peterson and
B. Davie, Morgan Kaufmann, 2007. |
 |
Computer Networks (4th Edition), Andrew S. Tanenbaum, Prentice Hall, 2003.
|
 |
Data and
Computer Communication (8th Edition),
William Stallings,
Prentice Hall, 2007. |
 |
Computer Networking with
Internet Protocols,
William Stallings, Prentice Hall, 2004. |
Tools and Development Environments
Grading (Tentative)
Course Grading:
30 % : Lab Experiments and Lab Exam
15
% :
Midterm Exam 1
20
% :
Midterm Exam 2
35 % : Final Exam (a comprehensive exam at the end of the
course)
Lab Grading:
Final Lab Grade = 50 % Lab Grades
Average + 50 % Lab Exam
 |
Lectures: Theoretical foundations and
background. |
 |
Lab Experiments:
The lab is
very important for a course of this kind. |
 |
Midterm Exam: There
will be one midterm exam. |
 |
Final Exam: There will
be one final exam covering all the materials learned in this course. It will be given during final exams period of the
semester. |
 |
Attendance, Discussion and
Contribution (ADC): Look at my Attendance Algorithm on the
Regulations page.
Additional Attendance Policy for Labs:
if your lab attendance < %80, you fail the lab (%25 of the
course grade becomes "0")
|
|